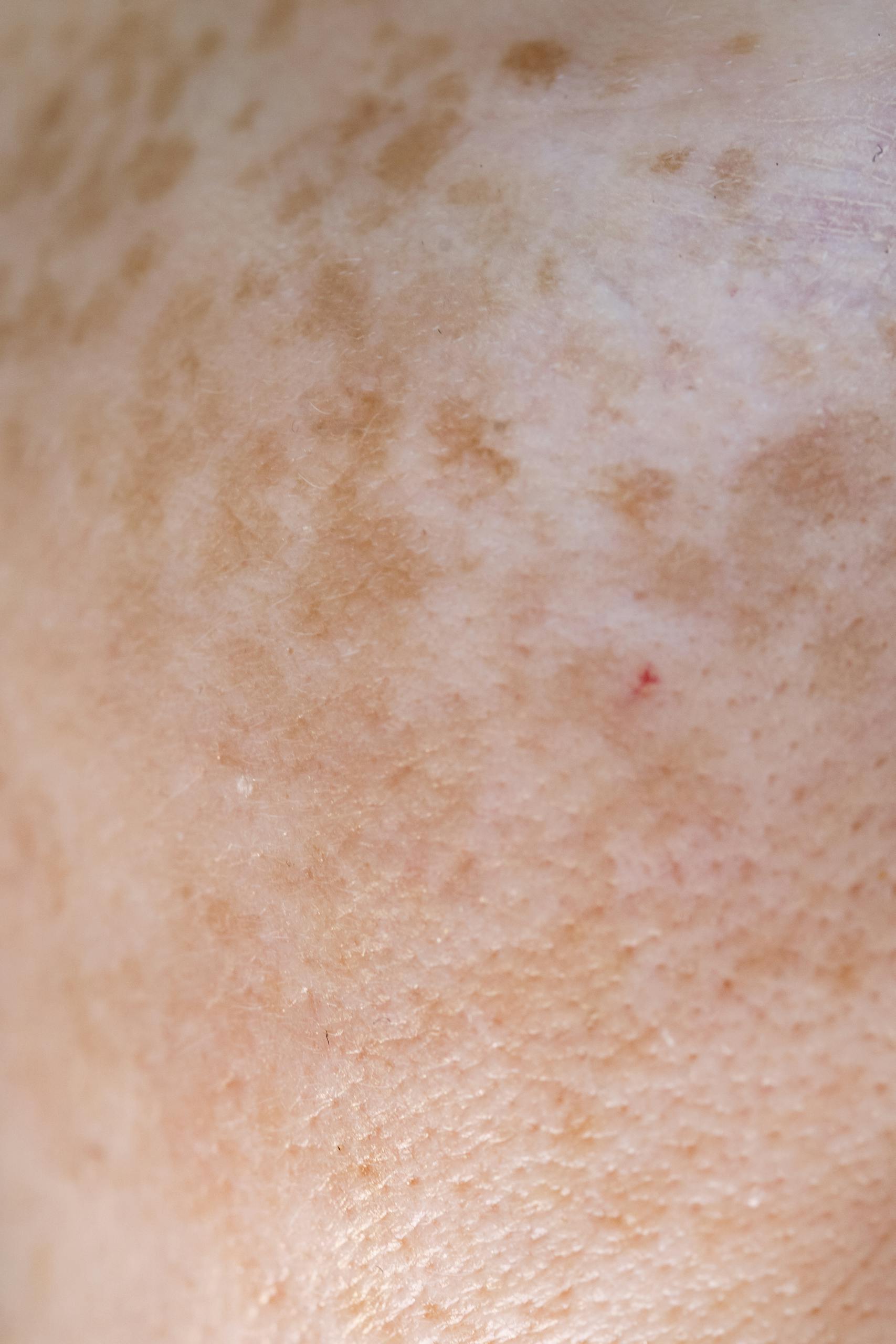
Hyperpigmentation in Perimenopause: Hormonal Causes and Highly Effective Treatments
Hyperpigmentation is a common and frustrating skin concern during perimenopause. As estrogen levels fluctuate, melanocytes—the pigment-producing cells in your skin—can become overactive, leading to dark spots, age spots, and melasma. Sun exposure, slower skin cell turnover, and inflammation can worsen these effects. The good news is that with the right ingredients and a consistent skincare routine, you can reduce dark spots, even skin tone, and maintain a radiant complexion.
This guide explores how hormones drive hyperpigmentation in perimenopause, the best OTC skincare ingredients, lifestyle strategies, and highly effective, dermatologist-favored products.
How Hormones Increase Hyperpigmentation in Perimenopause
Perimenopause typically begins in your 40s and lasts several years as your body transitions to menopause. During this phase, estrogen and progesterone levels fluctuate, which significantly affects your skin.
- Estrogen Decline and Melanin Overproduction
Estrogen regulates melanin synthesis. When estrogen drops, melanocytes can overproduce pigment, resulting in darker spots and uneven tone. This is why melasma—a type of hormonal hyperpigmentation—often appears during perimenopause. - Slower Skin Turnover
Estrogen promotes healthy skin cell turnover. As levels decline, old skin cells linger longer, making hyperpigmented spots more noticeable. - Increased UV Sensitivity
Lower estrogen reduces the skin’s natural defense against UV damage. Sun exposure can trigger new spots and worsen existing ones. - Inflammation and Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Hormonal changes can increase skin sensitivity. Even minor inflammation from acne, irritation, or dryness can leave dark marks that linger longer than they did in younger years.
Understanding these hormonal influences helps tailor your skincare routine for maximum effectiveness.
Highly Effective Skincare Ingredients for Hyperpigmentation
The following ingredients are OTC and highly rated, backed by dermatologists and clinical research for reducing hyperpigmentation.
1. Vitamin C (L-Ascorbic Acid)
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that inhibits melanin production, brightens the skin, and protects against free radical damage.
Recommended Products:
- La Roche-Posay Pure Vitamin C Face Serum – Known for its gentle formulation, this serum is suitable for sensitive skin and helps to reduce fine lines and brighten the complexion.
- Sunday Riley C.E.O. Glow Vitamin C + Turmeric Face Oil – a highly effective, dermatologist-favored product designed to brighten and even out skin tone, making it an excellent choice for addressing hyperpigmentation.
2. Niacinamide (Vitamin B3)
Niacinamide helps reduce melanin transfer to skin cells, improves barrier function, and calms inflammation.
Recommended Products:
- The Ordinary Niacinamide 10% + Zinc 1% – affordable and effective for brightening and oil control.
- Paula’s Choice 20% Niacinamide Booster – a strong formulation of niacinamide to brighten, improve texture, and minimize pores
3. Azelaic Acid
Azelaic acid lightens pigmentation by inhibiting tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for melanin production. It is also anti-inflammatory and safe for sensitive or acne-prone skin.
Recommended Products:
- The Ordinary Azelaic Acid Suspension 10% – Gentle yet effective for PIH and melasma.
- Paula’s Choice 10% Azelaic Acid Booster – A versatile booster that can be mixed into your favorite moisturizer or serum to target hyperpigmentation.
4. Retinol
Retinol accelerates cell turnover, fades dark spots, and improves skin texture. While prescription-strength tretinoin is not OTC, retinol products are safe and effective for perimenopausal skin.
Recommended Products:
- La Roche-Posay Retinol B3 Serum – combines retinol with niacinamide for gentle, effective results.
- Paula’s Choice 1% Retinol Booster – potent yet suitable for mature skin, minimizes irritation.
5. Tranexamic Acid
Tranexamic acid targets stubborn melasma and hormonal pigmentation by blocking pigment formation in melanocytes.
Recommended Products:
- The Inkey List Tranexamic Acid Night Treatment – reduces dark spots and blends well with other serums.
- Seonglow 15% Vegan Niacinamide + 3% Tranexamic Acid Serum is a potent Korean skincare serum designed to address hyperpigmentation and uneven skin tone.
6. Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs)
AHAs like glycolic and lactic acid exfoliate the surface of the skin, speeding up cell turnover and allowing dark spots to fade.
Recommended Products:
- Paula’s Choice 8% AHA Gel – gentle, effective exfoliation suitable for sensitive, mature skin.
- Sunday Riley Good Genes Lactic Acid Treatment – exfoliates and brightens, reducing visible pigmentation.
The Essential Role of Sun Protection
Sun protection is the single most important step in preventing and reducing hyperpigmentation.
Recommended Products:
- Avène Mineral SPF 50+ Sunscreen – gentle, non-comedogenic, broad-spectrum UV protection.
- La Roche-Posay Anthelios Melt-in Milk SPF 60 – highly rated for sensitive skin, prevents new dark spots.
Pro Tip: Apply daily, even indoors, and reapply every 2 hours when outdoors. Don’t forget ears, neck, and hands.
Sample Skincare Routine for Perimenopausal Hyperpigmentation
Morning Routine
- Gentle Cleanser – removes impurities without stripping moisture.
- Vitamin C Serum – protects against free radicals and brightens skin.
- Niacinamide Serum – evens skin tone and strengthens the barrier.
- Moisturizer – hydrates and prepares the skin for sunscreen.
- Sunscreen – essential to prevent UV-induced pigmentation.
Evening Routine
- Cleanser – removes sunscreen and makeup.
- Retinol or Bakuchiol Serum – accelerates cell turnover and reduces dark spots.
- Tranexamic Acid or Azelaic Acid Serum – targets stubborn hyperpigmentation.
- Moisturizer – locks in hydration and supports overnight repair.
Tip: Introduce one active ingredient at a time to monitor tolerance and avoid irritation.
Lifestyle and Dietary Tips
Beyond skincare, lifestyle choices significantly impact hyperpigmentation:
- Eat antioxidant-rich foods – berries, leafy greens, and green tea support skin repair.
- Stay hydrated – promotes cell regeneration and healthy skin barrier.
- Manage stress – high cortisol levels can exacerbate pigmentation.
- Get quality sleep – allows skin to repair and regenerate overnight.
Professional Options for Stubborn Hyperpigmentation
If OTC products aren’t enough, these professional options are safe alternatives:
- Chemical Peels (AHA or Mandelic Acid) – exfoliate skin and fade dark spots.
- Microneedling – enhances serum absorption and promotes collagen production.
- Laser Treatments (Non-ablative Lasers like Nd:YAG or Fraxel) – target melanin for stubborn spots.
Consult a dermatologist to tailor treatments to perimenopausal skin sensitivity.
Highly Rated, Effective Products Summary
| Product | Active Ingredient | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| La Roche-Posay Pure Vitamin C Face Serum | Vitamin C | Brightens, antioxidant protection |
| Sunday Riley C.E.O. Glow Vitamin C + Turmeric Face Oil | Vitamin C + Turmeric | Prevents new spots, brightens |
| The Ordinary Niacinamide 10% + Zinc 1% | Niacinamide | Evens skin tone, reduces PIH |
| La Roche-Posay Retinol B3 Serum | Retinol + Niacinamide | Cell turnover, smooths texture |
| Paula’s Choice 10% Azelaic Acid Booster | Azelaic Acid | Reduces dark spots, soothes |
| The Inkey List Tranexamic Acid Night Treatment | Tranexamic Acid | Targets melasma and stubborn pigmentation |
| Sunday Riley Good Genes Lactic Acid Treatment | Glycolic Acid | Gentle exfoliation, brighter skin |
| Avène Mineral SPF 50+ Sunscreen | Zinc Oxide | Prevents UV-induced hyperpigmentation |
FAQs
Q: Can hormonal changes during perimenopause really worsen dark spots?
A: Yes. Fluctuating estrogen increases melanin production, slows skin turnover, and makes your skin more UV-sensitive.
Q: How long before I see results?
A: With consistent use of OTC ingredients like Vitamin C, retinol, niacinamide, and azelaic acid, improvements often appear within 8–12 weeks.
Q: Can I combine multiple actives?
A: Yes, but introduce one active at a time (e.g., retinol at night, Vitamin C in the morning) and patch test to avoid irritation.
Conclusion
Hyperpigmentation in perimenopause is largely driven by hormonal fluctuations that increase melanin production, slow skin turnover, and make your skin more UV-sensitive. Using OTC, highly effective ingredients such as Vitamin C, niacinamide, azelaic acid, tranexamic acid, and retinol, along with strict sun protection, can significantly improve dark spots and even skin tone.
Combining targeted skincare, supportive lifestyle habits, and safe professional options when needed can help perimenopausal women regain a brighter, more radiant complexion.